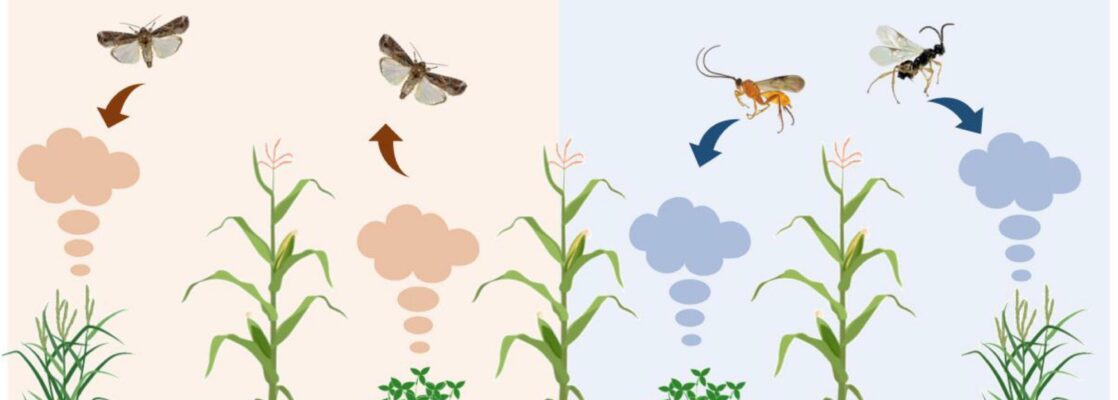
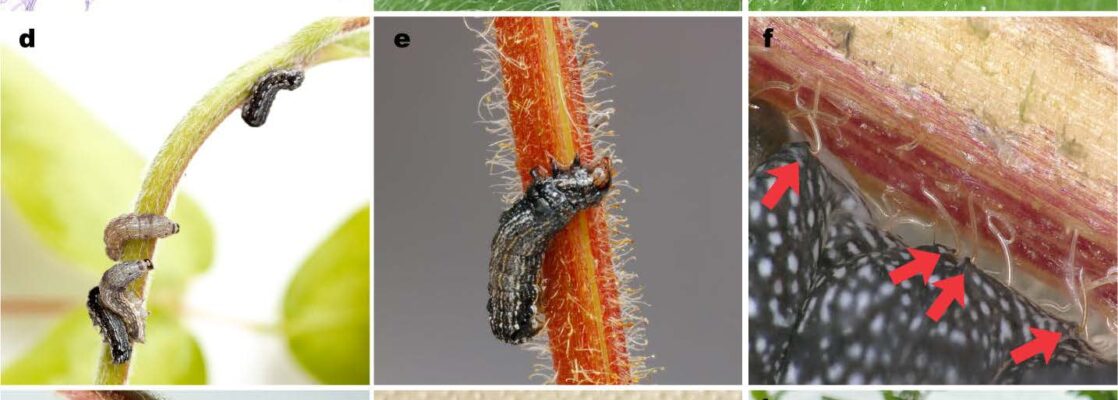
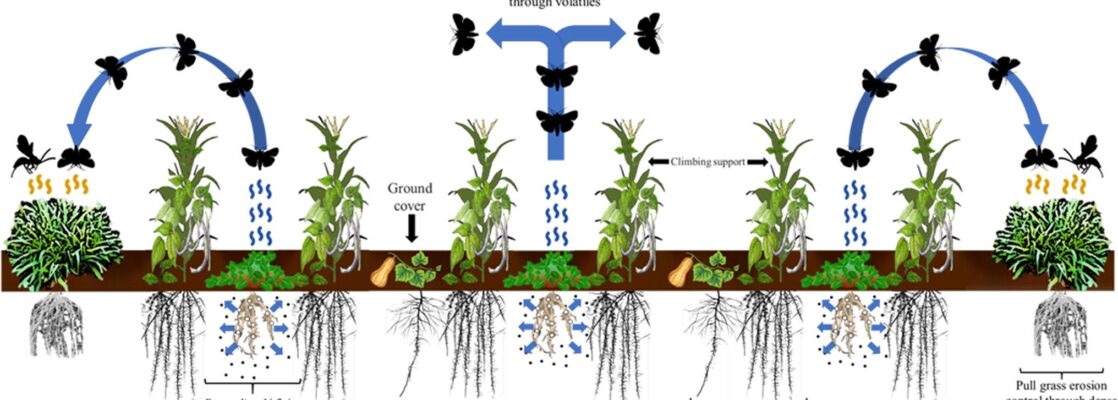
Our data provide evidence of the mechanisms underpinning reduced S. frugiperda infestation in the Push-Pull companion cropping system, i.e., volatiles from companion crops repel S. frugiperda while attracting its parasitoid natural enemies. These findings explain why Push-Pull field plots had fewer S. frugiperda larvae and lower crop damage than monocropped maize.