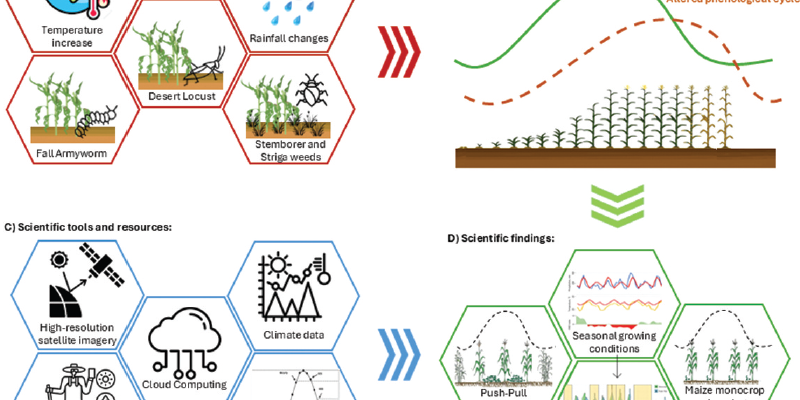
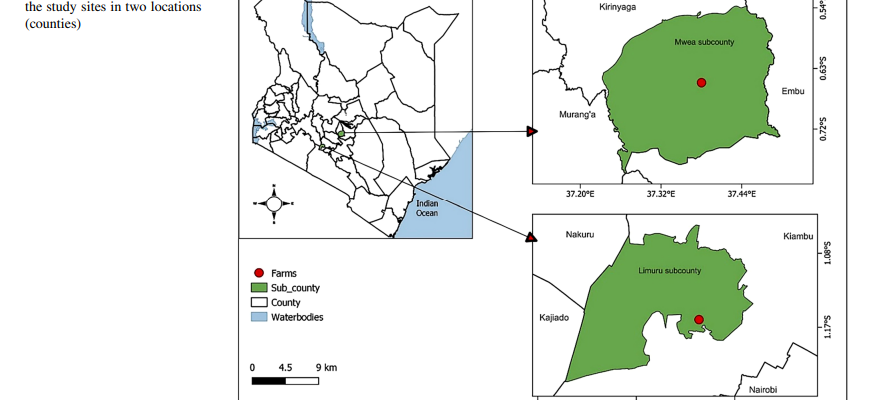
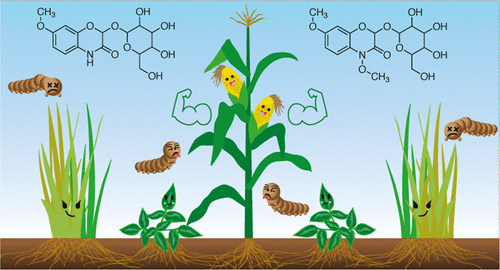
This review aims to appraise the PPT used in eastern Africa, synthesize evidence for its ecological and economic benefits, and identify barriers to its adoption and opportunities for its expansion to other crops and farming systems in sub-Saharan Africa.