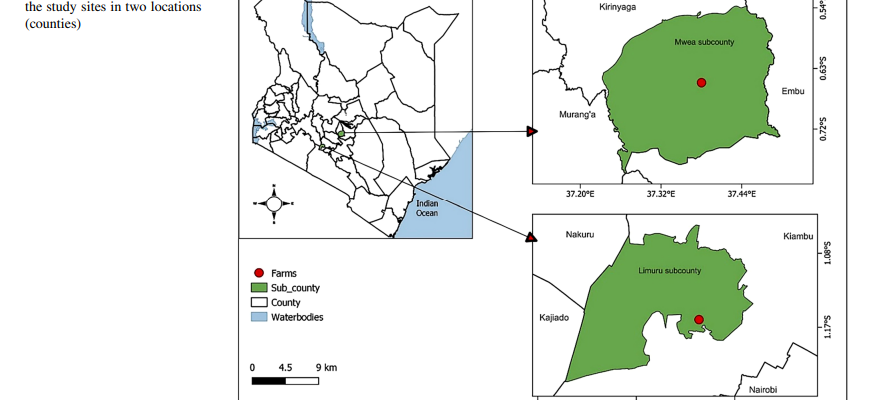
The fall armyworm (FAW), Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith), causes significant damage to maize, threatening the food security and livelihood of millions of smallholder farmers in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA). Crop diversification has been recommended as an ecologically sustainable FAW control option. However, limited information is available on the impacts of companion plants and their control mechanisms against FAW in SSA, being a relatively new pest to the region. Building upon our earlier laboratory study, which elucidated how edible companion intercrops effectively reduce FAW infestation, we conducted field experiments in Kenya to assess the effectiveness of intercropping maize with beans, groundnut, cassava and sweet potato under realistic field conditions. Growing maize with these intercrops consistently resulted in fewer FAW eggs, larvae and lower plant infestation compared to maize monoculture except with cassava. Additionally, maize under these intercrops experienced low FAW damage and higher crop yield compared to maize monoculture. Maize growth stages significantly influenced the population of FAW eggs and larvae, with a peak observed between vegetative stages V4 and V10. Furthermore, intercropped maize plots exhibited a higher presence of FAW predators, such as lady beetles and earwigs. Correlation analysis revealed a significant correlation between temperature, relative humidity, and the population of FAW life stages and natural enemies at the experimental sites. Therefore, intercropping maize with beans, sweet potato, and groundnuts can be incorporated into an integrated FAW management strategy to sustainably control the pest in real farming conditions. These findings are particularly relevant for small-scale farmers in Africa and beyond, who cannot afford expensive FAW control using insecticides.
Authors: Emmanuel Peter, Abdullahi Yusuf, Sevgan Subramanian, Kerstin Krüger, Kristina Karlsson Green, Peter Anderson, Baldwyn Torto, Amanuel Tamiru
Contact address: tamiru@icipe.org
Institution: International Centre of Insect Physiology and Ecology (icipe), Nairobi, Kenya
Twitter name of the institution: @icipe
Twitter link: https://x.com/icipe
Available downloads: