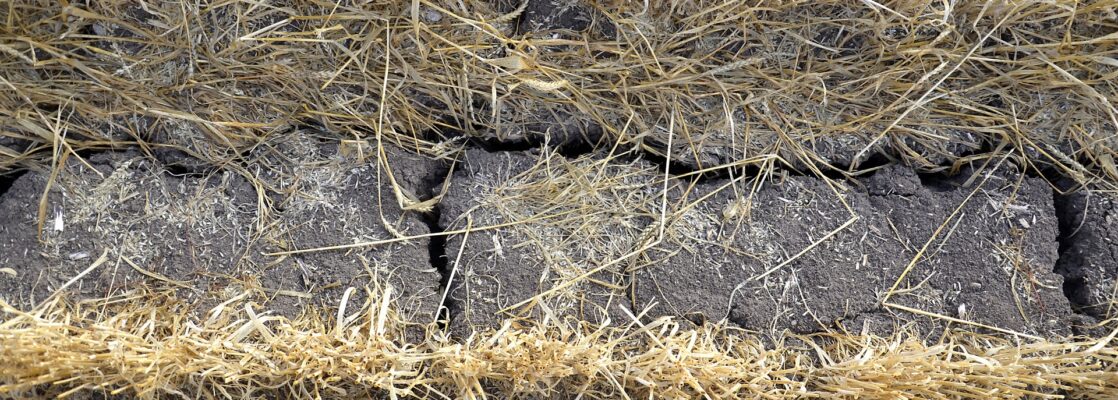
Soil degradation is a major underlying cause of poverty and malnutrition in smallholder agricultural communities across the globe. Legume diversification, through polyculture or intercropping, is a strategy that increases yields and income while improving family nutrition. However, the potential for these legume-cereal intercrops to restore soil functions in smallholder fields remains uncertain, with many studies failing to detect increases in soil organic matter (SOM). In sub-Saharan Africa, smallholders typically grow maize either intercropped with short-lived annual food legumes or as a monoculture. Recently, a novel maize system which includes perennial legumes in the genus Desmodium as intercrops, known as “push-pull” (hereafter, PP) has been increasingly adopted by smallholders across the region.
The PP system’s yield, nutritional and economic benefits are well documented. We investigated the effects of PP maize intercropping on soil fertility compared to the predominant maize culture systems (hereafter, NPP) using soils from long-term experiments and smallholder fields in western Kenya. Maize-desmodium intercrops promoted SOM accrual and increased plant available phosphorus. In the long-term research station experiments soil organic N was 20% greater and labile organic N reserves were five-fold greater in PP compared to NPP soils. Despite equal P fertilizer application rates, extractable soil P was two-fold greater in PP compared to NPP soils.
Soils under maize-food legume intercrops did not show any detectable accrual of SOM compared to maize monocultures. Soil benefits in smallholder PP fields mirror those found in the controlled experiments. Taken together, our results demonstrate that the perennial legumes in the PP system restore soil function and fertility. Developing additional well-designed intercropping systems that include perennial legumes could play a significant role in reversing the trajectory of soil degradation in smallholder farming systems while enhancing human well-being.
Authors: Laurie E. Drinkwater, Charles A.O. Midega, Rachel Awuor, Dickens Nyagol & Zeyaur R. Khan
Contact address: led24@cornell.edu
Institution: Cornell University, School of Integrated Plant Science-Horticulture Section; www.cornell.edu
Twitter name of the institution: @Cornell
Twitter link: https://twitter.com/icipe
Available downloads